Delve into The American Pageant Chapter 1 Notes, an unparalleled resource that unveils the tapestry of American history, from its European roots to the complexities of the modern era. This comprehensive guide empowers you to grasp the pivotal events, influential figures, and enduring legacies that have shaped the United States.
Embark on a journey through time, exploring the motivations behind European exploration, the impact of colonization on indigenous peoples, and the birth of the American republic. Witness the transformative power of the Industrial Revolution, the challenges of the Civil War, and the transformative movements of the Progressive Era.
European Exploration and Colonization

The European Age of Exploration, which began in the 15th century, was a period of intense maritime exploration by European powers. The primary motivations for this exploration were the search for new trade routes, the acquisition of wealth and resources, and the spread of Christianity.
Major European Powers Involved in Colonization
The major European powers involved in colonization were Spain, Portugal, England, France, and the Netherlands. These countries established colonies in the Americas, Africa, and Asia, and their influence had a profound impact on the indigenous peoples of these regions.
Impact of European Colonization on the Indigenous Peoples of the Americas, The american pageant chapter 1 notes
The arrival of European colonizers in the Americas had a devastating impact on the indigenous peoples. The introduction of European diseases, the displacement of indigenous populations, and the exploitation of natural resources led to a significant decline in the indigenous population.
Additionally, European colonizers often imposed their own cultural and political systems on the indigenous peoples, leading to the loss of traditional languages, customs, and beliefs.
The American Revolution
The American Revolution was a pivotal conflict that resulted in the thirteen American colonies declaring independence from Great Britain. This transformative event shaped the political landscape of North America and had a profound impact on global history.
Causes of the American Revolution
The American Revolution was sparked by a complex interplay of political, economic, and social factors. These included:
- British policies that limited colonial autonomy and economic growth
- Rising tensions between the colonists and British authorities
- Growing sense of American identity and nationalism
Key Events of the American Revolution
The American Revolution unfolded through a series of key events, including:
- The Boston Tea Party (1773)
- The Battle of Lexington and Concord (1775)
- The Declaration of Independence (1776)
- The Battle of Saratoga (1777)
- The Battle of Yorktown (1781)
Significance of the American Revolution
The American Revolution had a profound impact on the United States and the world:
- Established the United States as an independent nation
- Inspired revolutions in other parts of the world
- Strengthened the principles of democracy and self-government
- Led to the development of a new American identity
The Early Republic
The formation of the United States of America marked a new era in global politics and the establishment of a unique republican government. The early years of the republic were characterized by both challenges and opportunities as the nation sought to establish its identity, expand its territory, and define its political system.
Challenges Faced by the New American Republic
The new republic faced numerous challenges in its early years, including:
Establishing a stable and effective government
The United States was the first nation to adopt a written constitution and a republican form of government. Creating a system that could effectively balance power and protect individual rights was a complex task.
Financing the government
The new government lacked a stable source of revenue and struggled to fund its operations and pay off its debts.
Defending the nation’s borders
The United States was bordered by hostile Native American tribes and rival European powers. Protecting the nation’s territory and citizens required a strong military.
Maintaining unity among the states
The United States was a diverse nation with different economic interests and political views. Balancing the needs of the individual states with the needs of the nation as a whole was a constant challenge.
Development of Political Parties in the United States
One of the most significant developments in the early republic was the emergence of political parties. The first two major parties were the Federalists, led by Alexander Hamilton, and the Democratic-Republicans, led by Thomas Jefferson.
- The Federalists favored a strong central government and a close relationship with Great Britain.
- The Democratic-Republicans favored a weaker central government and a more limited role for the federal government in the lives of citizens.
The competition between these two parties shaped the political landscape of the United States for decades to come.
Westward Expansion of the United States
Another defining characteristic of the early republic was the westward expansion of the United States. As the population grew and the nation’s economy expanded, settlers began to move west in search of land and opportunity.
- The Louisiana Purchase of 1803 doubled the size of the United States and opened up vast new territories for settlement.
- The Lewis and Clark Expedition of 1804-1806 explored the Louisiana Purchase and provided valuable information about the geography and resources of the West.
- The Indian Removal Act of 1830 forced Native American tribes to relocate west of the Mississippi River, opening up even more land for settlement.
The westward expansion of the United States had a profound impact on the nation’s history and culture, shaping its identity as a land of opportunity and Manifest Destiny.
The Civil War
The Civil War, fought from 1861 to 1865, was a watershed moment in American history. It pitted the Union, comprised of Northern and Western states, against the Confederacy, composed of eleven Southern states. The war’s primary cause was the profound disagreement over the issue of slavery, with the North advocating for its abolition and the South determined to preserve it.
Causes of the Civil War
- Slavery: The institution of slavery was the central issue that divided the North and South. The Northern states had largely abolished slavery, while the Southern economy relied heavily on it.
- Economic Differences: The North had a more industrialized and diversified economy, while the South was primarily agrarian. This disparity led to differing views on economic policy, including tariffs and infrastructure.
- Political Differences: The North and South had different views on the role of the federal government. The North favored a strong central government, while the South advocated for states’ rights.
Key Events of the Civil War
The Civil War was a bloody and protracted conflict, with major battles taking place across the country. Key events included:
- Battle of Fort Sumter(1861): The Confederate attack on Fort Sumter in South Carolina marked the beginning of the war.
- Battle of Gettysburg(1863): This pivotal battle was a Union victory that turned the tide of the war in favor of the North.
- Emancipation Proclamation(1863): President Abraham Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation, freeing slaves in Confederate-held territory.
- Battle of Appomattox Court House(1865): Confederate General Robert E. Lee surrendered to Union General Ulysses S. Grant, effectively ending the war.
Impact of the Civil War
The Civil War had a profound impact on the United States:
- Abolition of Slavery: The war resulted in the abolition of slavery and the passage of the 13th Amendment to the Constitution.
- Strengthened Federal Government: The war strengthened the federal government and increased its authority over the states.
- Reconstruction: After the war, the United States entered a period of Reconstruction, during which it attempted to rebuild the South and integrate freed slaves into society.
- Legacy of Division: The Civil War left a lasting legacy of division and sectionalism in American society.
The Industrial Revolution: The American Pageant Chapter 1 Notes
The Industrial Revolution, which originated in Great Britain in the late 18th century, profoundly transformed the United States. This era witnessed the emergence of new technologies, mass production, and the growth of cities.
Causes of the Industrial Revolution
- Agricultural Revolution:Improved farming techniques led to increased food production, freeing up labor for industrial work.
- Technological Innovations:Inventions such as the steam engine, cotton gin, and power loom accelerated production.
- Capitalism and Free Enterprise:The rise of capitalism provided incentives for investment and innovation.
- Abundant Natural Resources:The United States possessed vast amounts of coal, iron ore, and timber, essential for industrial growth.
Impact on American Society
The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on American society:
- Urbanization:Industrial jobs attracted people to cities, leading to rapid urban growth.
- Economic Growth:Mass production boosted productivity and economic output.
- Social Inequality:Industrialization created a divide between wealthy factory owners and low-paid workers.
- Environmental Degradation:Factories polluted the air and water, contributing to environmental problems.
Rise of Labor Unions
In response to poor working conditions and low wages, workers began to organize into labor unions.
- Reasons for Unionization:Exploitation of workers, unsafe working conditions, and low pay.
- Tactics:Unions used strikes, boycotts, and collective bargaining to improve their lot.
- Impact:Labor unions played a significant role in securing better wages, working conditions, and social benefits for workers.
The Progressive Era
The Progressive Era, spanning from the late 19th century to the early 20th century, marked a period of significant social and political reforms in the United States. Driven by a widespread belief in progress and the power of human agency, Progressives sought to address the problems created by industrialization, urbanization, and political corruption.
Goals of the Progressive Era
The primary goals of the Progressive Era included:
- Promoting social justice and economic equality
- Improving the lives of working-class Americans
- Curbing the power of large corporations
- Reforming government to make it more responsive to the needs of the people
Key Reforms of the Progressive Era
Progressives implemented a wide range of reforms, including:
- Labor laws to protect workers’ rights and safety
- Food and drug regulations to ensure the safety of consumer products
- Women’s suffrage, granting women the right to vote
- Direct election of senators, giving voters a more direct voice in government
- The Federal Reserve System, established to stabilize the financial system
Impact of the Progressive Era on American Society
The Progressive Era had a profound impact on American society, leading to:
- Improved living conditions for working-class Americans
- Increased government regulation of the economy
- Expanded political participation, particularly for women
- A shift in American values towards a greater emphasis on social justice and equality
The United States in the 20th Century
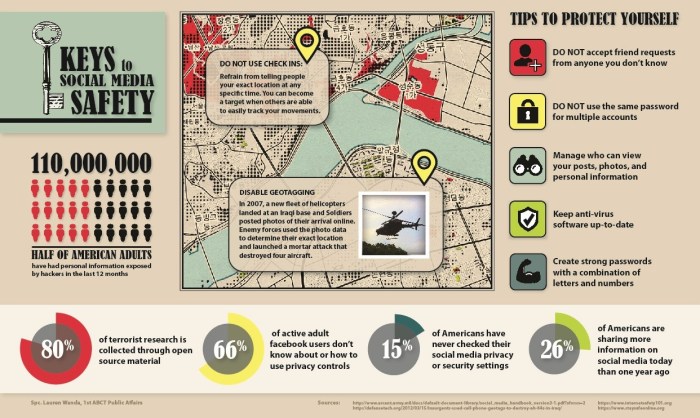
The 20th century was a period of great change and upheaval for the United States. The country emerged from World War I as a global power and played a major role in World War II. The United States also experienced significant social and economic changes during this time, including the Great Depression and the Civil Rights Movement.
The United States’ Entry into World War I
The United States entered World War I in 1917 after Germany resumed unrestricted submarine warfare in the Atlantic Ocean. This policy threatened American shipping and led to the sinking of several American ships, including the passenger liner Lusitania. The United States also became increasingly concerned about Germany’s growing power in Europe and its alliance with Mexico.
The Impact of World War I on the United States
World War I had a profound impact on the United States. The war led to the deaths of over 100,000 Americans and caused significant economic disruption. The war also led to the passage of the Espionage Act and the Sedition Act, which restricted free speech and dissent.
However, the war also helped to boost the American economy and led to the emergence of the United States as a global power.
The United States’ Role in World War II
The United States entered World War II in 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. The United States played a major role in the Allied victory over the Axis powers. The war led to the deaths of over 400,000 Americans and caused significant economic disruption.
However, the war also helped to boost the American economy and led to the emergence of the United States as a superpower.
The Cold War
The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, which began after the Second World War and lasted from 1947 to 1991. The term “cold” is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they engaged in a series of proxy wars and other forms of indirect conflict.
Causes of the Cold War
- Ideological differences between the United States and the Soviet Union, with the US promoting capitalism and democracy and the USSR promoting communism and authoritarianism.
- The Soviet Union’s expansion into Eastern Europe after World War II, which the US saw as a threat to its security.
- The US’s atomic bomb monopoly, which gave it a significant advantage over the USSR.
Key Events of the Cold War
- The Berlin Blockade (1948-1949): The Soviet Union blockaded West Berlin in an attempt to force the Western Allies out of the city.
- The Korean War (1950-1953): A proxy war between the US and the USSR that ended in a stalemate.
- The Cuban Missile Crisis (1962): A standoff between the US and the USSR over the Soviet Union’s deployment of nuclear missiles in Cuba.
- The Vietnam War (1955-1975): A proxy war between the US and the USSR that ended in a US defeat.
- The Détente (1969-1979): A period of reduced tensions between the US and the USSR.
- The Soviet-Afghan War (1979-1989): A proxy war between the US and the USSR that ended in a Soviet defeat.
Impact of the Cold War on the United States
- The Cold War led to a massive increase in military spending and the development of new weapons technologies.
- It also led to a period of heightened political tension and fear of nuclear war.
- The Cold War had a profound impact on American culture, leading to the rise of McCarthyism and the Red Scare.
The Civil Rights Movement

The Civil Rights Movement was a period of social activism and protest that aimed to end racial discrimination and segregation in the United States. It began in the mid-20th century and lasted for several decades.The causes of the Civil Rights Movement were complex and varied.
One major factor was the legacy of slavery and Jim Crow laws, which had created a system of racial segregation and discrimination that permeated all aspects of American society. Another factor was the growing awareness of the civil rights movement in other parts of the world, particularly in India and Africa.
Finally, the movement was fueled by the growing economic and political power of African Americans.The key events of the Civil Rights Movement included the Montgomery Bus Boycott, the March on Washington, and the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965. These events helped to bring about significant changes in American society, including the desegregation of schools and public facilities, the expansion of voting rights, and the end of legal discrimination.The
impact of the Civil Rights Movement on American society was profound. It helped to create a more just and equitable society, and it laid the foundation for further progress in the years to come.
The United States in the 21st Century
The United States has faced numerous challenges in the 21st century, including economic inequality, political polarization, and climate change. Despite these challenges, the country has also experienced significant progress in areas such as technology, healthcare, and education.
Economic Inequality
Economic inequality has been a growing problem in the United States for decades. The gap between the rich and the poor has widened, and the middle class has been shrinking. This inequality has been caused by a number of factors, including the decline of manufacturing jobs, the rise of the service economy, and the increasing cost of education and healthcare.
Political Polarization
Political polarization has also increased in the United States in recent years. The two major political parties, the Democrats and the Republicans, have become increasingly divided on a wide range of issues, including healthcare, immigration, and climate change. This polarization has made it difficult for the government to address the country’s challenges.
Climate Change
Climate change is another major challenge facing the United States. The country is already experiencing the effects of climate change, such as rising sea levels, more extreme weather events, and changes in plant and animal life. These effects are expected to become more severe in the future, and they could have a significant impact on the country’s economy, infrastructure, and way of life.
Key Events of the 21st Century
The 21st century has been a time of significant change for the United States. Some of the key events of the century include:* The September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks
- The wars in Afghanistan and Iraq
- The Great Recession
- The election of Barack Obama as the first African American president
- The rise of social media
- The COVID-19 pandemic
These events have had a profound impact on the United States, and they have shaped the country’s politics, economy, and culture.
The Future of the United States
The future of the United States is uncertain. The country faces a number of challenges, but it also has a number of strengths. The United States is a resilient country with a strong economy, a diverse population, and a commitment to democracy.
If the country can overcome its challenges, it has the potential to continue to be a leading force in the world.
Key Questions Answered
What are the key themes explored in The American Pageant Chapter 1?
The chapter examines European exploration, colonization, the American Revolution, the formation of the republic, and the challenges of westward expansion.
How does the chapter highlight the impact of European colonization on indigenous peoples?
The chapter discusses the devastating consequences of European diseases, warfare, and displacement on Native American populations.
What were the major causes of the American Revolution?
The chapter identifies British taxation policies, imperial control, and the desire for self-governance as key factors.