Label the spinal cord meninges and spaces. – The spinal cord, a crucial component of the central nervous system, is enveloped by three protective layers known as the meninges. These meninges, along with the spaces between them, play a vital role in safeguarding the delicate spinal cord from external forces and facilitating its proper functioning.
This article delves into the anatomy and clinical significance of the spinal cord meninges and spaces, providing a comprehensive overview for medical professionals and students alike.
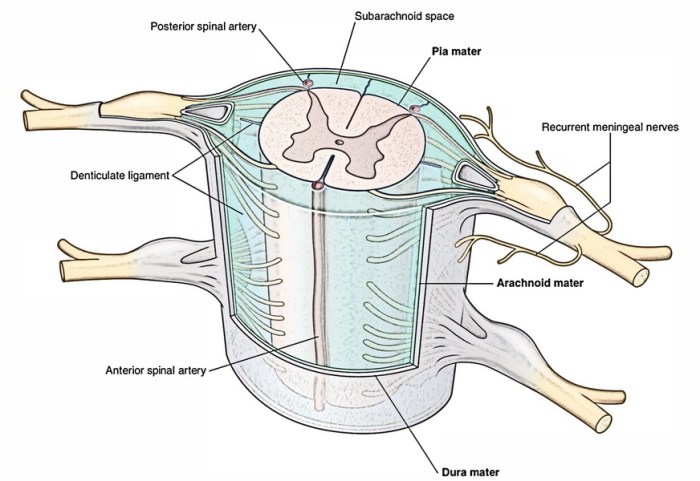
The meninges consist of three distinct layers: the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Each layer possesses unique structural characteristics and functions, contributing to the overall protection and support of the spinal cord. Additionally, two spaces exist within the meninges: the subarachnoid space and the epidural space.
These spaces are filled with cerebrospinal fluid, which provides cushioning and nourishment to the spinal cord.
Label the Spinal Cord Meninges and Spaces: Label The Spinal Cord Meninges And Spaces.
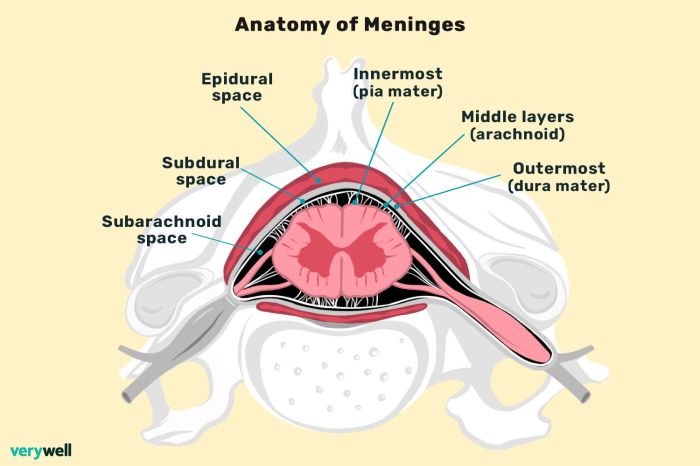
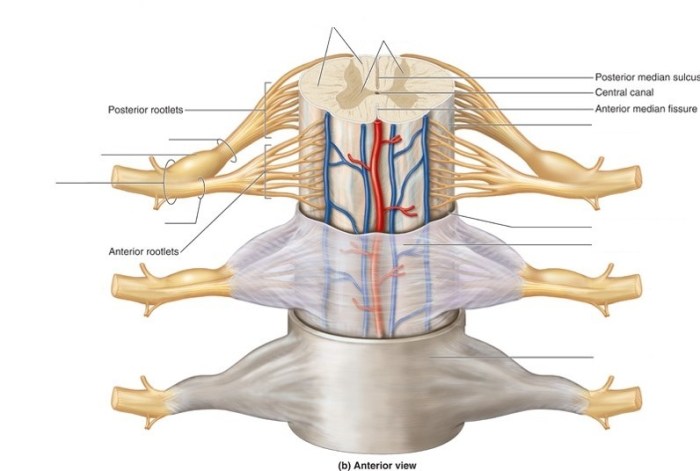
The spinal cord is protected by three layers of meninges, which are membranes that line the spinal canal and surround the spinal cord. These layers are the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater.
Label the Spinal Cord Meninges
| Meninges Layer | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Dura Mater | The outermost layer of the meninges, it is a tough, fibrous membrane that lines the spinal canal and surrounds the spinal cord. | Protects the spinal cord from mechanical injury. |
| Arachnoid Mater | A delicate, web-like membrane that lies deep to the dura mater. | Forms the subarachnoid space, which contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). |
| Pia Mater | The innermost layer of the meninges, it is a thin, vascular membrane that adheres closely to the surface of the spinal cord. | Provides nutrients to the spinal cord and helps to anchor it in place. |
Label the Spinal Cord Spaces
| Space Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Subarachnoid Space | The space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater, which is filled with CSF. | Protects the spinal cord from mechanical injury and provides a pathway for the flow of CSF. |
| Epidural Space | The space between the dura mater and the bony wall of the spinal canal, which is filled with fat and blood vessels. | Provides a cushion for the spinal cord and allows for the passage of blood vessels and nerves. |
Clinical Significance of the Spinal Cord Meninges and Spaces, Label the spinal cord meninges and spaces.
The meninges play a vital role in protecting the spinal cord from injury. They act as a barrier to infection and help to cushion the spinal cord from mechanical forces. Injuries to the meninges can lead to serious complications, such as meningitis or spinal cord compression.
The spaces within the spinal cord are also clinically important. The subarachnoid space is the site of lumbar punctures, which are used to collect CSF for diagnostic purposes. The epidural space is the site of epidural injections, which are used to relieve pain.
Question Bank
What are the three layers of the spinal cord meninges?
The three layers of the spinal cord meninges are the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater.
What is the function of the subarachnoid space?
The subarachnoid space contains cerebrospinal fluid, which cushions and nourishes the spinal cord.
What is the clinical significance of the epidural space?
The epidural space is clinically significant because it is the site of epidural anesthesia, which is commonly used during childbirth and surgical procedures.