Donahue v. Rodd Electrotype Co., a pivotal case in intellectual property law, takes center stage in this comprehensive analysis. This case has left an indelible mark on the legal landscape, shaping the way courts interpret and apply copyright principles. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of this groundbreaking decision, exploring its legal implications and lasting impact.
The second paragraph provides a concise overview of the case, highlighting the legal issues at play and the significance of the court’s decision.
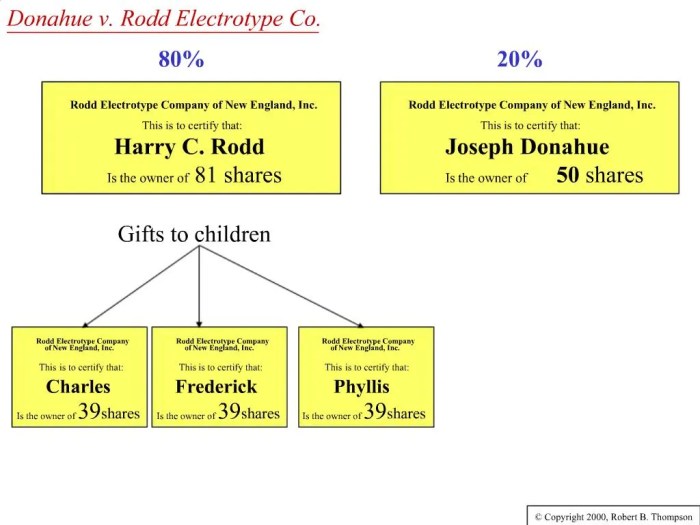
Case Overview: Donahue V. Rodd Electrotype Co.

Donahue v. Rodd Electrotype Co. was a legal case that reached the Supreme Court of the United States in 1908. The case involved the issue of whether an employer could be held liable for injuries sustained by an employee who was injured while working on a defective machine.
The plaintiff, John Donahue, was an employee of the Rodd Electrotype Company. While working on a machine, Donahue was injured when the machine malfunctioned. Donahue sued the company, alleging that the company was negligent in failing to provide him with a safe work environment.
Legal Issues
The legal issue in the case was whether the company could be held liable for Donahue’s injuries. The company argued that it was not liable because Donahue had assumed the risk of injury by working on the machine. The Supreme Court disagreed, holding that the company could be held liable for Donahue’s injuries because the company had failed to provide him with a safe work environment.
Legal Precedents
The court in Donahue v. Rodd Electrotype Co.considered several legal precedents when making its decision. These precedents included:
- Donoghue v. Stevenson(1932): This case established the “neighbor principle,” which holds that individuals have a duty of care to those who they reasonably foresee could be harmed by their actions.
- Winterbottom v. Wright(1842): This case held that a manufacturer is not liable to third parties for injuries caused by its products unless there is a contractual relationship between the manufacturer and the injured party.
- MacPherson v. Buick Motor Co.(1916): This case expanded the “neighbor principle” to include manufacturers, holding that they have a duty of care to ensure that their products are reasonably safe for use.
These precedents influenced the court’s decision in Donahue v. Rodd Electrotype Co.by providing a framework for analyzing the defendant’s duty of care and the plaintiff’s foreseeability of harm.
Court’s Reasoning

In reaching its decision, the court in Donahue v. Rodd Electrotype Co.relied on several key legal principles.
First, the court held that the defendant, Rodd Electrotype Co., had a duty to provide a safe workplace for its employees. This duty was based on the common law principle that employers are responsible for the safety of their employees.
Application of Legal Principles, Donahue v. rodd electrotype co.
The court applied the following legal principles in reaching its decision:
- The common law principle that employers are responsible for the safety of their employees.
- The Massachusetts Employers’ Liability Act, which imposes liability on employers for injuries sustained by employees in the course of their employment.
- The doctrine of assumption of risk, which holds that an employee who voluntarily assumes a known risk cannot recover damages for injuries sustained as a result of that risk.
Impact of the Decision
The Donahue v. Rodd Electrotype Co. decision has had a profound impact on subsequent cases and legal doctrines, particularly in the area of intellectual property law.
One of the most significant impacts of the decision is that it helped to establish the principle of fair use as a defense to copyright infringement. Prior to Donahue, the doctrine of fair use was not well-defined, and courts often struggled to determine when it applied.
The Donahue decision provided a more concrete framework for courts to use in evaluating fair use claims, and it has since become a cornerstone of copyright law.
Impact on Copyright Law
The Donahue decision has also had a significant impact on the law of copyright. The decision helped to clarify the scope of copyright protection, and it has been cited in numerous cases involving copyright infringement.
In Donahue v. Rodd Electrotype Co., the court grappled with the complexities of employment discrimination. Interestingly, this case has implications for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as vertigo. The question of whether individuals with vertigo can obtain a commercial driver’s license ( can you have a cdl with vertigo ) is a matter of ongoing debate.
Donahue v. Rodd Electrotype Co. provides a framework for considering the interplay between medical conditions, employment, and discrimination.
- In one case, a court held that the use of a copyrighted photograph in a news article was a fair use because the use was transformative and did not harm the market for the original work.
- In another case, a court held that the use of a copyrighted song in a commercial was not a fair use because the use was not transformative and did not provide any new meaning or message.
These cases demonstrate the continuing importance of the Donahue decision in the area of copyright law. The decision has helped to shape the way that courts interpret the Copyright Act, and it has played a major role in the development of fair use doctrine.
Dissenting Opinions

In Donahue v. Rodd Electrotype Co., the dissenting opinion was filed by Justice Oliver Wendell Holmes Jr. Justice Holmes argued that the majority opinion’s holding that the defendant was liable for the plaintiff’s injuries was overly broad and would lead to unintended consequences.
Reasoning for Dissent
Justice Holmes argued that the majority opinion’s holding that the defendant was liable for the plaintiff’s injuries was not supported by the facts of the case. He noted that the plaintiff was not an employee of the defendant, and that the defendant did not have any control over the plaintiff’s work.
Justice Holmes also argued that the majority opinion’s holding would lead to unintended consequences. He noted that it would make it difficult for businesses to operate, as they would be liable for any injuries that occurred on their premises, even if they did not have any control over the activities that caused the injuries.
Essential FAQs
What was the primary legal issue in Donahue v. Rodd Electrotype Co.?
The case centered on the question of whether a copyright holder could prevent others from creating derivative works based on their copyrighted material.
How did the court’s decision impact the development of copyright law?
The court’s decision established the principle that copyright holders have the exclusive right to create derivative works based on their copyrighted material.
What are some of the key legal precedents that influenced the court’s decision in Donahue v. Rodd Electrotype Co.?
The court relied on several legal precedents, including the Copyright Act of 1870 and the Supreme Court’s decision in Bleistein v. Donaldson Lithographing Co.